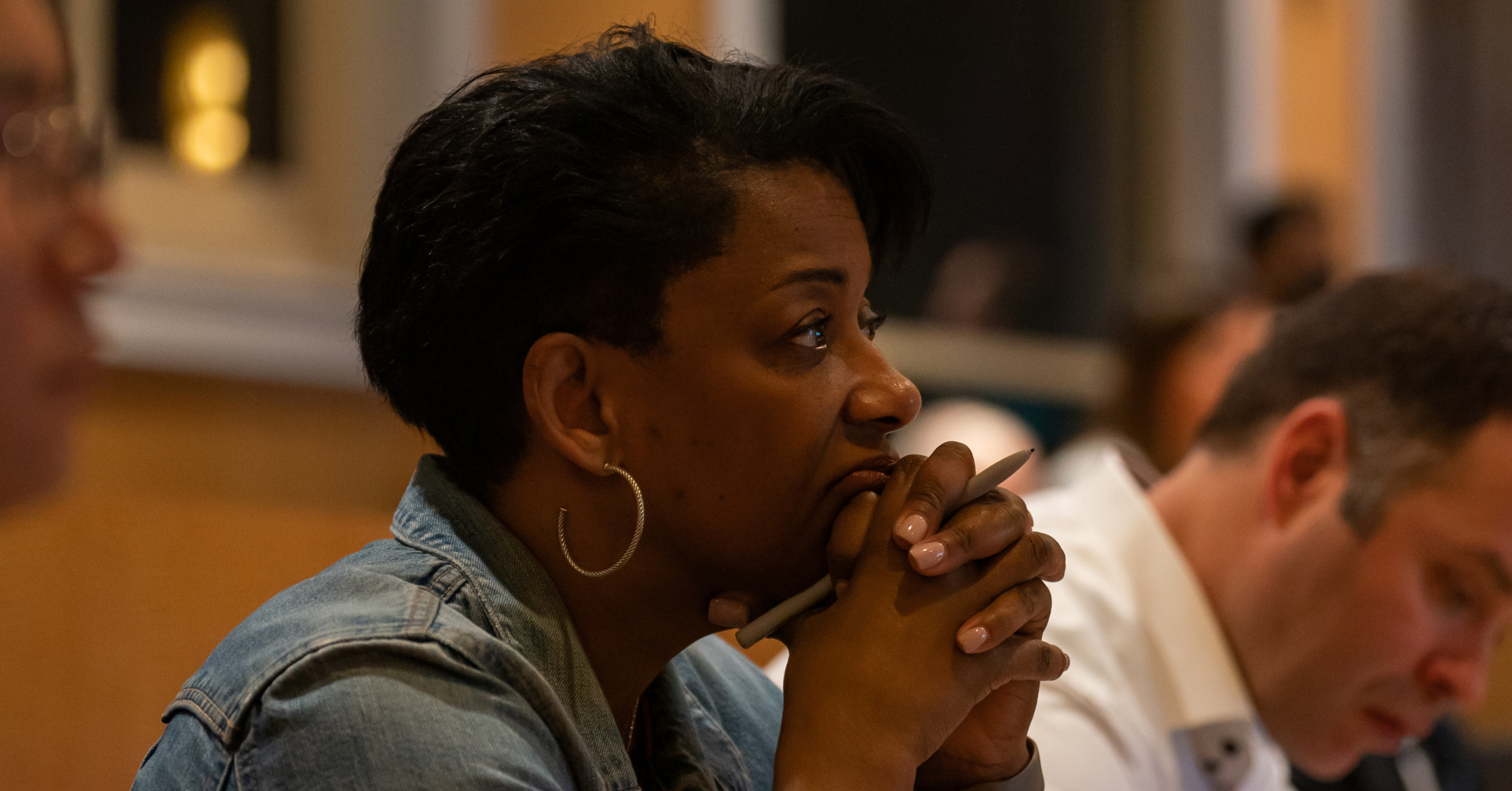
Amidst all of our individual stories, we have witnessed moments of courage and a lifetime of hope with our fundamental wish being to see a future where bone marrow failure bone marrow failure: A condition that occurs when the bone marrow stops making enough healthy blood cells. The most common of these rare diseases are aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Bone marrow failure can be acquired (begin any time in life) or can be… disease is treatable.
- 1983
- 1984
- 1989
- 1993
- 1994
- 1997
- 1999
- 2000
- 2002
- 2004
- 2005
- 2006
- 2007
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2011
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2022
- Now
1983 »
Orphan Drug Orphan Drug: A drug or biologic agent that treats a rare disease or condition. A disease is considered rare if fewer than 200,000 people in the United States have it. Act Bill is approved and President Reagan signs into law in January, 1983.
Parents of young aplastic anemia aplastic anemia: (ay-PLASS-tik uh-NEE_mee-uh) A rare and serious condition in which the bone marrow fails to make enough blood cells - red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The term aplastic is a Greek word meaning not to form. Anemia is a condition that happens when red blood cell count is low. Most… patient establish the Aplastic Anemia Foundation with the help of physicians from Johns Hopkins University.
« 1984 »
Orphan Drug Act Amendment: rare disease is defined as fewer than 200,000 diagnosed annually.
« 1993 »
The Aplastic Anemia Foundation establishes a Medical Advisory Board. Founding members who are still serving include Dr. Neal Young and Dr. Joachim Deeg.
« 1994 »
Foundation expands its scope to create educational materials and a volunteer network for MDS patients and families.
« 2000 »

NIH Establishes clinicaltrials.gov
Foundation officially changes its name to the Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation (AAMDSIF).
« 2002 »
Rare Diseases Act signed establishing the NIH Rare Disease Clinical Research Clinical Research: A type of research that involves individual persons or a group of people. There are three types of clinical research. Patient-oriented research includes clinical trials which test how a drug, medical device, or treatment approach works in people. Epidemiology or behavioral studies look at the… Network.
First Patient and Family Conference held in Denver, Colorado.
« 2005 »

FDA approves Revlimid® (lenalidomide) as a therapy for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes myelodysplastic syndromes: (my-eh-lo-diss-PLASS-tik SIN-dromez) A group of disorders where the bone marrow does not work well, and the bone marrow cells fail to make enough healthy blood cells. Myelo refers to the bone marrow. Dysplastic means abnormal growth or development. People with MDS have low blood cell count for at… (MDS).
FDA approves Exjade® (deferasirox) as a once daily oral iron chelator approved for chronic iron overload iron overload: A condition that occurs when too much iron accumulates in the body. Bone marrow failure disease patients who need regular red blood cell transfusions are at risk for iron overload. Organ damage can occur if iron overload is not treated. due to blood transfusion dependent thalassemia.
First International Scientific Symposium is held in the greater Washington, D.C. area with world-renowned faculty.
« 2007 »
FDA approves Soliris® (eculizumab) as a therapy for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: (par-uk-SIZ-muhl nok-TURN-uhl hee-muh-gloe-buh-NYOOR-ee-uh) A rare and serious blood disease that causes red blood cells to break apart. Paroxysmal means sudden and irregular. Nocturnal means at night. Hemoglobinuria means hemoglobin in the urine. Hemoglobin is the red part of red blood cells. A… (PNH).
« 2008 »
First collaboration with Cleveland Clinic at the annual American Society of Hematology conference.
« 2009 »

Inaugural March for Marrow Indianapolis is organized. Previously called Hope, Steps and a Cure.
30 research grants awarded since 2000.
« 2010 »
Rare disease office established at the FDA: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Office of New Drugs.
« 2011 »

The MDS Update newsletter is published connecting patients and families with news, research, and expert opinions.
« 2012 »

The MDS Clinical Research Consortium is established with funding received from the Edward P. Evans Foundation. Members include Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Dana-Farber Cancer Center, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine Leukemia Program.
« 2015 »

AAMDSIF establishes The Patient Advisory Committee for Clinical Trials Clinical Trials: Clinical research is at the heart of all medical advances, identifying new ways to prevent, detect or treat disease. If you have a bone marrow failure disease, you may want to consider taking part in a clinical trial, also called a research study. Understanding Clinical Trials Clinical… (PACCT+) with a grant received from The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
« 2017 »

AAMDSIF held its first International Regional Bone Marrow Failure Disease Symposium in León, Guanajuato, Mexico.
« 2018 »
Since 1989, AAMDSIF has awarded 92 research grants focused on bone marrow failure disease totaling more than $5M.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved ravulizumab-cwvz ravulizumab-cwvz: Ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris®) is a drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 to treat PNH. ULTOMIRIS® is a long-acting C5 inhibitor that works by inhibiting the C5 protein in the terminal complement cascade. ULTOMIRIS® is a prescription medicine called a… (ULTOMIRIS) for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria hemoglobinuria: (hee-muh-gloe-buh-NYOOR-ee-uh) The presence of hemoglobin in the urine. (PNH) in adult patients.
« 2019 »
AAMDSIF launched the Map of Specialists for patients to find an expert in their disease.
AAMDSIF hosted its first podcast - Podcast for Patients series.
AAMDSIF began offering all educational materials for digital download.
« 2020 »
AAMDSIF took the lead by offering a COVID-19 webinar for patients diagnosed with bone marrow failure only 10 days after the lockdown was declared.
AAMDSIF began offering virtual support groups for patients and families in April.
AAMDSIF held its first all-virtual, interactive, Patient and Family Conference in April.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved luspatercept-aamt luspatercept-aamt: REBLOZYL® (luspatercept-aamt) is the first erythroid maturation agent (EMA) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and European Union for the treatment of anemia in adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) who have been failed by an erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) or… (REBLOZYL, Celgene Corporation) for the treatment of anemia anemia: (uh-NEE-mee-uh) A condition in which there is a shortage of red blood cells in the bloodstream. This causes a low red blood cell count. Symptoms of anemia are fatigue and tiredness. failing an erythropoiesis stimulating agent and requiring 2 or more red blood cell red blood cell: The most numerous type of blood cell in healthy people. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that picks up oxygen in the lungs and brings it to cells in all parts of the body. Also called erythrocyte, RBC. (RBC) units over 8 weeks in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS) or with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine) tablets for treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.
« 2021 »
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Empaveli (pegcetacoplan) injection to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a rare, life-threatening blood disease. Empaveli is the first PNH treatment that binds to complement protein C3.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Ultomiris (ravulizumab-cwvz) injection to treat patients aged one month and older with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Ultomiris is the first PNH treatment approved for children.
AAMDSIF Launched Global PNH Patient Registry.
« 2022 »
AAMDSIF held its first hybrid conference for patients and families utilizing an interactive platform for online participation.
AAMDSIF created a free, downloadable, health emergency card.
GVHD Interactive Provider Network began.
Initial Health Professionals Conference: Providing Equitable and Inclusive Care to Patients with Bone Marrow Failure.
AAMDSIF creates Aplastic Anemia and PNH patient toolkits.
AAMDSIF awards 100th Research Grant.
« Now
Created the "Living with PNH" feature to help PNH patients manage life after diagnosis.
Now more than 40 years later, the Foundation continues its work serving as the patient voice in advocacy and partnering with the pharmaceutical industry. We provide education and information to health professionals and patients diagnosed with aplastic anemia, MDS, PNH, and AML.
1983 »
Orphan Drug Act Bill is approved and President Reagan signs into law in January, 1983.
Parents of young aplastic anemia patient establish the Aplastic Anemia Foundation with the help of physicians from Johns Hopkins University.
« 1984 »
Orphan Drug Act Amendment: rare disease is defined as fewer than 200,000 diagnosed annually.
« 1993 »
The Aplastic Anemia Foundation establishes a Medical Advisory Board. Founding members who are still serving include Dr. Neal Young and Dr. Joachim Deeg.
« 1994 »
Foundation expands its scope to create educational materials and a volunteer network for MDS patients and families.
« 2000 »

NIH Establishes clinicaltrials.gov
Foundation officially changes its name to the Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation (AAMDSIF).
« 2002 »
Rare Diseases Act signed establishing the NIH Rare Disease Clinical Research Network.
First Patient and Family Conference held in Denver, Colorado.
« 2005 »

FDA approves Revlimid® (lenalidomide) as a therapy for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
FDA approves Exjade® (deferasirox) as a once daily oral iron chelator approved for chronic iron overload due to blood transfusion dependent thalassemia.
First International Scientific Symposium is held in the greater Washington, D.C. area with world-renowned faculty.
« 2007 »
FDA approves Soliris® (eculizumab) as a therapy for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
« 2008 »
First collaboration with Cleveland Clinic at the annual American Society of Hematology conference.
« 2009 »

Inaugural March for Marrow Indianapolis is organized. Previously called Hope, Steps and a Cure.
30 research grants awarded since 2000.
« 2010 »
Rare disease office established at the FDA: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Office of New Drugs.
« 2011 »

The MDS Update newsletter is published connecting patients and families with news, research, and expert opinions.
« 2012 »

The MDS Clinical Research Consortium is established with funding received from the Edward P. Evans Foundation. Members include Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Dana-Farber Cancer Center, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine Leukemia Program.
« 2015 »

AAMDSIF establishes The Patient Advisory Committee for Clinical Trials (PACCT+) with a grant received from The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
« 2017 »

AAMDSIF held its first International Regional Bone Marrow Failure Disease Symposium in León, Guanajuato, Mexico.
« 2018 »
Since 1989, AAMDSIF has awarded 92 research grants focused on bone marrow failure disease totaling more than $5M.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved ravulizumab-cwvz (ULTOMIRIS) for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) in adult patients.
« 2019 »
AAMDSIF launched the Map of Specialists for patients to find an expert in their disease.
AAMDSIF hosted its first podcast - Podcast for Patients series.
AAMDSIF began offering all educational materials for digital download.
« 2020 »
AAMDSIF took the lead by offering a COVID-19 webinar for patients diagnosed with bone marrow failure only 10 days after the lockdown was declared.
AAMDSIF began offering virtual support groups for patients and families in April.
AAMDSIF held its first all-virtual, interactive, Patient and Family Conference in April.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved luspatercept-aamt (REBLOZYL, Celgene Corporation) for the treatment of anemia failing an erythropoiesis stimulating agent and requiring 2 or more red blood cell (RBC) units over 8 weeks in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS) or with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine) tablets for treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.
« 2021 »
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Empaveli (pegcetacoplan) injection to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a rare, life-threatening blood disease. Empaveli is the first PNH treatment that binds to complement protein C3.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Ultomiris (ravulizumab-cwvz) injection to treat patients aged one month and older with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Ultomiris is the first PNH treatment approved for children.
AAMDSIF Launched Global PNH Patient Registry.
« 2022 »
AAMDSIF held its first hybrid conference for patients and families utilizing an interactive platform for online participation.
AAMDSIF created a free, downloadable, health emergency card.
GVHD Interactive Provider Network began.
Initial Health Professionals Conference: Providing Equitable and Inclusive Care to Patients with Bone Marrow Failure.
AAMDSIF creates Aplastic Anemia and PNH patient toolkits.
AAMDSIF awards 100th Research Grant.
« NOW
Created the "Living with PNH" feature to help PNH patients manage life after diagnosis.
Now more than 40 years later, the Foundation continues its work serving as the patient voice in advocacy and partnering with the pharmaceutical industry. We provide education and information to health professionals and patients diagnosed with aplastic anemia, MDS, PNH, and AML.